Blog

Medical credentialing plays a critical role in ensuring safe, ethical, and compliant care across the behavioral health field. For treatment centers, therapists, counselors, psychiatrists, and other behavioral health professionals, proper credentialing determines whether they can legally provide services, bill insurance, and participate in payer networks. As reimbursement rules tighten and payers increase oversight, understanding medical credentialing in mental health is essential for financial stability and continuity of care.
At Hansei Solutions, we help mental health and substance use treatment providers navigate the credentialing process to ensure compliance and prevent costly disruptions. Below, we break down how credentialing works, what the process includes, and why it is becoming more important than ever.
What Is Medical Credentialing?
Medical credentialing is the process of verifying a provider’s education, training, licenses, certifications, and professional experience to ensure they are qualified to deliver clinical care. Insurance companies, regulatory agencies, and healthcare organizations require credentialing to:
- Confirm provider competence
- Maintain patient safety
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Prevent fraudulent claims
- Authorize participation in insurance networks
In mental health treatment, credentialing applies to:
- Psychiatrists
- Psychologists
- Nurse practitioners
- Therapists and counselors
- Clinical social workers
- Addiction specialists
- Behavioral health technicians (depending on state rules)
Without credentialing, providers cannot bill insurance—and treatment centers risk significant compliance and reimbursement issues.
Why Credentialing Matters in Mental Health Care
Credentialing is especially important in behavioral health because of the sensitive nature of mental health treatment and the variability in provider licensure regulations across different states.
- Credentialing protects patients – It ensures that clinicians meet educational, ethical, and training standards required for safe care.
- Credentialing protects providers – It confirms that a clinician is legally allowed to practice and reduces liability exposure.
- Credentialing protects treatment centers – Billing insurance without properly credentialed providers can result in denials, audits, recoupments, and compliance violations.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), credentialing is one of the primary safeguards used to maintain quality and safety in healthcare delivery systems.
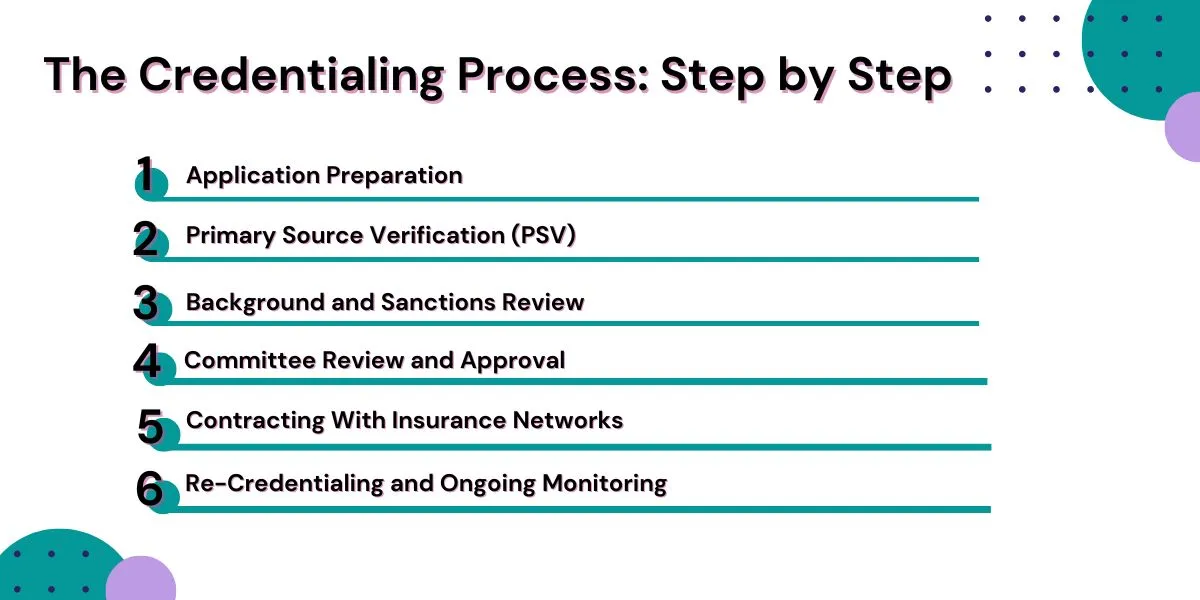
The Credentialing Process: Step by Step
Credentialing involves several detailed steps that must be completed accurately to avoid delays. These steps vary slightly by payer but generally follow the same structure.
Step 1: Application Preparation
The provider submits all required documents, which often include:
- Professional licenses
- Board certifications
- Education transcripts
- Clinical training records
- National Provider Identifier (NPI)
- Resume/CV
- Background disclosures
- Proof of malpractice insurance
Missing or outdated documents are a major cause of credentialing delays.
Step 2: Primary Source Verification (PSV)
PSV is the heart of the credentialing process. Insurance companies and credentialing bodies verify the information directly with the issuing institutions.
This includes verification of:
- Medical degrees or graduate education
- Residency or clinical training
- State licensure
- DEA registration (if applicable)
- Malpractice history
- Certification status
The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) requires PSV for all credentialed providers, and this process can take several weeks depending on provider history and completeness of documents.
Step 3: Background and Sanctions Review
Payers review provider records through federal and state databases such as:
- OIG Exclusion List
- National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB)
- State licensure boards
- Medicaid/Medicare exclusion lists
This step ensures providers have no disciplinary actions preventing them from delivering care.
Step 4: Committee Review and Approval
Credentialing committees—at hospitals, treatment centers, or insurance companies—evaluate the verified information and determine whether the provider meets their standards.
Committee review often includes:
- Scope of practice review
- Competency evaluation
- Clinical experience review
- Peer references
Once approved, the provider is credentialed but may still need additional steps to join payer networks.
Step 5: Contracting With Insurance Networks
Credentialing and contracting are separate processes. After credentialing, a provider must sign a contract with the payer to become an in-network, reimbursable provider.
This step includes:
- Fee schedules
- Reimbursement terms
- Network participation rules
- Documentation and billing requirements
Only after contracting can the provider bill as in-network.
Step 6: Re-Credentialing and Ongoing Monitoring
Credentialing isn’t a one-time event. Most payers require re-credentialing every 2–3 years, along with ongoing monitoring for licensure status, disciplinary actions, and compliance.
NCQA and CMS both require organizations to track changes in provider credentials continuously, not just during renewal periods.
How Long Does Medical Credentialing Take?
Credentialing timelines vary, but most range from 60 to 120 days, depending on:
- Payer requirements
- Provider history
- State regulations
- Completeness of documentation
According to CAQH, U.S. healthcare organizations spend over $2.76 billion annually on credentialing-related administrative work—much of which results from repeated data entry or missing information.
A single mistake can delay network participation for weeks or even months, causing financial strain for treatment centers.

Common Challenges in Behavioral Health Credentialing
Mental health providers face unique hurdles during the credentialing process:
- Multiple licenses and varying state requirements – Regulations differ across states, requiring detailed record-keeping and updates.
- Incomplete or inconsistent documentation – Missing CEU records, outdated malpractice certificates, or incomplete CVs cause delays.
- Payer-specific rules that change frequently – Insurance companies adjust credentialing rules annually.
- Long processing times – Behavioral health networks often have limited capacity for review, slowing approval times.
- Difficulty credentialing new hires quickly – Delays prevent providers from billing, impacting revenue and scheduling.
This is why many treatment centers partner with credentialing experts to manage the process effectively.
The Role of Hansei Solutions in Credentialing Support
Credentialing issues create major financial challenges for behavioral health providers. At Hansei Solutions, we support credentialing by helping providers:
- Prepare accurate documentation
- Track expirations and renewals
- Navigate payer-specific requirements
- Reduce errors that lead to delays
- Ensure providers meet compliance standards
- Coordinate CAQH attestation updates
- Monitor network participation and deadlines
With payers tightening oversight, strong credentialing workflows are essential to prevent denials, reduce administrative burden, and support long-term sustainability.
Why Credentialing Is Essential for Behavioral Health Reimbursement
Credentialing directly impacts:
- Timely reimbursement
- Provider scheduling
- Authorization approvals
- Compliance readiness
- Risk mitigation
- Network expansion and patient access
Uncredentialed or incorrectly credentialed providers put treatment centers at risk for:
- Denials
- Recoupments
- Network exclusion
- Loss of patient trust
- Legal and regulatory consequences
Credentialing is not just paperwork—it’s the foundation of safe, ethical, and financially sustainable mental healthcare.
FAQs: Medical Credentialing in Mental Health Treatment
Why is credentialing important for mental health providers?
Credentialing ensures a provider is qualified, licensed, and authorized to deliver care and bill insurance. It protects patients, providers, and treatment centers by maintaining clinical and regulatory standards.
How long does credentialing take?
Most credentialing processes take between 60 and 120 days, depending on payer response times and the completeness of documentation.
Is credentialing the same as contracting?
No. Credentialing verifies qualifications, while contracting establishes the provider’s reimbursement rates and in-network status.
What happens if a provider isn’t credentialed?
Claims may deny, and the treatment center may face compliance risks or recoupments. Providers may also be unable to see certain patients.
Does Hansei Solutions help with credentialing?
Yes. Hansei supports credentialing preparation, documentation, monitoring, and payer-specific navigation as part of our comprehensive revenue cycle services.
Support Your Credentialing Process With Hansei Solutions
Whether you’re onboarding new clinicians or navigating payer network requirements, credentialing doesn’t have to slow your organization down. At Hansei Solutions, we help behavioral health providers take control of their credentialing workflow so they can focus on delivering high-quality care. Talk to Hansei Solutions about improving your credentialing process.
Ready to focus on providing healthcare? Let us lighten your load.
We’re here to address your pain points and create growth opportunities for your organization. We’re passionate about what we do, and it shows in every interaction. Learn what makes us tick and schedule a demo today.